About
The Earth is a unique planet full of water and life including human beings, and has a history of 4.6 billion years. Environmental protection has become a global and urgent topic, and people hope to use the earth’s system more effectively without destroying it. The College of Geoscience offers English and Japanese programs for a Bachelor of Science in Geoscience to acquire general knowledge and insight into the evolution of the Earth, the natural processes on the Earth, and the interactions between natural environments and human activities, which would be the basis for the development of sustainable society.
English Program

The University of Tsukuba is the only university in Japan offering a degree in geoscience in English. The 4-year program in English started in 2011 and is now well established.
The program is aimed at students who hold a non-Japanese passport. Knowledge of Japanese is not expected.
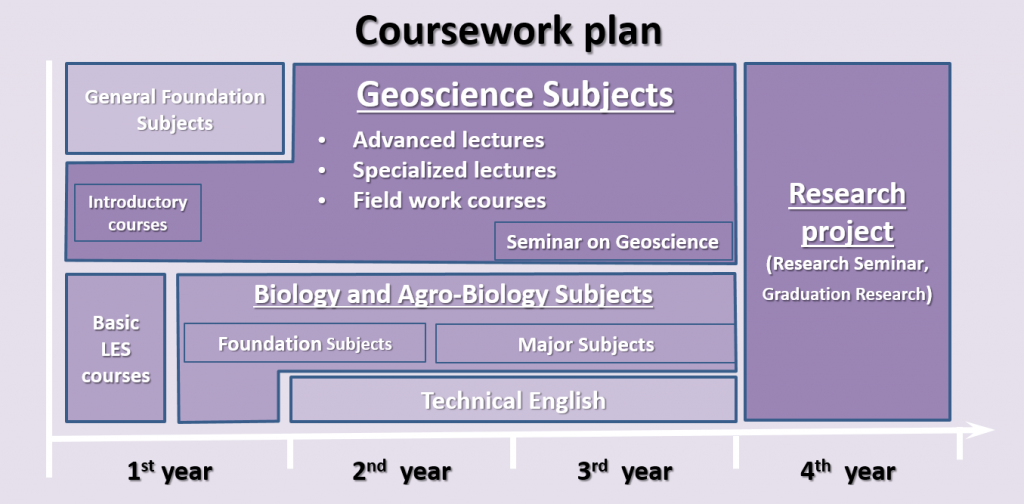
Coursework Plan
The English educational program allows students to overview diverse fields of geoscience. Students learn concepts, ideas and techniques of geoscience through a variety of course types.
Students are required to complete a minimum of 124 credits to graduate. Credits are categorized into subjects offered by
a.) the School of Life and Environmental Sciences (Geoscience, Biological Sciences and Agro-Biological Resource Sciences) making up two-thirds of the credit load and
b.) other Schools as “General Foundation Subjects” for the other third.
One lecture credit represents 10 lectures, with each lecture being 75 minutes long. For each hour of class time, students are expected to complete 3 hours of self-study for lectures and seminars.
The coursework plan is described below in detail.
General Foundation Subjects
Between 19 and 40 credits are invested into comprehensive general learning and cultural knowledge, with 19 credits mandatory as:
- Japanese language education offered at various proficiency levels (4 credits)
- Information Literacy (4 credits)
- Physical Education (2 credits)
- Art Practice (1 credit)
- Multidisciplinary Subjects (8 credits, mainly first year level)
The other 0 to 23 credits are elective courses chosen by students from the course offerings of the College of Social Sciences, the College of International Studies, the Language Center (excluding own native language(s)), in the Interdisciplinary Engineering Program, or physical education. Most of such credits are typically taken in the first two semesters.
Subjects of Life and Environmental Sciences
“Basic Knowledge and Techniques Common to Natural Sciences and to Life and Environmental Sciences“
In the first part of the program, students revise or acquire basic knowledge and techniques common to natural sciences and to Life and Environmental Sciences specifically. Geoscience students choose 8.5 credits from:
- Field Studies in Life and Environmental Sciences
- Mathematics
- Advanced Mathematics
- Physics
- Statistics
- Chemistry I, II, III
- Biology I, III, IV, V (Biology II has been transferred into a different course category)
Introductory Courses on Geoscience
The following four introductory courses on geoscience in the 1st semester are mandatory:
- Freshman Seminar in Geoscience I and II
- Introduction to Geoenvironmental Science
- Introduction to Earth Evolution Science
- Laboratory Work in Basic Geoscience
Advanced Geoscience Courses
In the following phase, students choose their own balance of courses offered in geoscience, biological sciences and agro-biological resource sciences.
The College offers 67 geoscience credits. The minimum credit load of advanced geoscience courses is 28, whereas students typically choose around 55 geoscience credits in total.
The graduation research yields only 10 credits (Research Seminar, Graduation Research, and Paper Preparation and Presentation) but lasts for a full year. Therefore geoscience students typically invest 55% of their study time into geoscience, the remaining for General Foundation Subjects and courses in biology and agro-biology.
Advanced lectures
From the second semester students take advanced lectures on each geoscience field which are offered mostly biannually. Those lectures are:
- Lecture on Geographical Information Systems
- Geomorphology
- Environmental Hydrology
- Meteorology & Climatology
- Human and Regional Geography
- Basic Analysis of Environmental Dynamics
- Mineralogy & Petrology
- Inorganic Geochemistry
- Paleontology & Stratigraphy
- Applied Structural Geology
Specialized lectures
These advanced lectures on each geoscience field are supplemented by specialized lectures:
- Natural Hazards
- Geomorphological Landscapes of the World
- GIS in Geomorphology
- Process Geomorphology
- Soil Erosion
- Quaternary Environmental Change
- Topics on Earth Evolution Science A, B (varying content)
- Topics on Geoenvironmental Science A, B (varying content)
- Topics on Geoscience A, B, C, D, E (varying content)
To learn techniques students choose Next to fieldwork methods, students also apply techniques and procedures used for data analysis and information processing. 6 fieldwork credits are mandatory although students can choose more. Most fieldwork courses are set as 1.5 credits, which relates to 5 days in the field excluding travel to the field site. The following fieldwork courses are offered typically every second or third year:
- Field Work in Geoenvironmental Science I, II, III, IV, V, VI (one course per field in Geoenvironmental Science)
- Field Work in Earth Evolution Science A, B, C, D, E, F, G




Internship Program
Students can also earn two credits for an internship program which allows students to acquire work experience in a company or research institute related to their majors or future careers. Students can enroll in internship programs as part of a job search. The opportunity to learn through experience in the real world makes internships very useful.
Subjects in Biological Sciences and Agro-Biological Resource Sciences
Students select 10-33 credits of foundation subjects in Biological Sciences and Agro-Biological Resource Sciences. Such include plant taxonomy, genome biology, marine biology, plant physiology, metabolic and physiological chemistry, world food and agriculture, cell structure and function, biochemistry, economics, vector disease biology and other courses.
Higher-level major subjects in biology and agro-biology are chosen after foundation subjects are taken. A minimum of 3 credits is required, while students have the choice to take a maximum of 48 credits – thus reducing geoscience courses. The following list only includes geoscience-related courses:
Vertebrate evolution, plant taxonomy II, marine biology II, genome biology III, chemical ecology, theoretical ecology; soil science, environmental ecological engineering, water environmental management technology, water resource management engineering, soil and water bio-engineering, economics of resource and environment.
Graduation Research

Before students start their research project, the Seminar on Geoscience A provides an overview of all laboratories of the College of Geoscience in a third-year level course. At the end of the Seminar on Geoscience B students choose their laboratory for graduation research. From the second to the third year students are trained in 6 credits of Technical English on how to write a thesis/ publication and how to make oral and poster presentations.
These two steps enable students to focus on a research project under the supervision of a faculty member during the final year of their degree (Graduation Research A and B). Students have access to well-equipped labs, and are advised by qualified, experienced researchers. The research methods comprise fieldwork, laboratory experiments and computer simulation. During the final year students present topics on geoscience and their research progress is discussed with members of a laboratory in the Research Seminar A and B. Students submit a graduation thesis at the end of the project and present their work either as a poster presentation or oral presentation to fellow students and academic staff.
Examples of research project titles

- Chaotic Sediments and Their Genesis of the Ishido Formation, Boso Peninsula, Central Japan (supervised by Prof. Ken-ichiro Hisada)
- Comparison of the Structure of Mid-latitude Cyclone (supervised by Prof. Hiroshi Tanaka)
- Behavior of the turbidity current under influence of the wave (supervised by Prof. Tomohiro Sekiguchi)
- Geomorphic process variability in mountain collapses (yamakuzure) and its effects on sediment production and sediment delivery in a headwater catchment in the Southern Japanese Alps (supervised by Prof. Thomas Parkner)
- Influence of deep-seated and shallow mass movements on gully formation in the lower Mangaoporo catchment, East Coast region, New Zealand (supervised by Prof. Thomas Parkner)
- A study on the Influence of the Metro Line Stations on Land-use and Land-Use-Change: A Case Study of Metro Line 1 in Hangzhou City (supervised by Prof. Yuji Maruyama)
- Taxonomy of the Latest Jurassic Pyloniacea (Radiolarian) (supervised by Prof. Katsuo Sashida)
Early Graduation
Students enter in September of their first year and complete six semesters of taught courses. The final year is mainly reserved for a research project resulting in a mandatory graduation thesis. Students who have accumulated sufficient credits with a high GPA can apply for early graduation, completing the four-year course in 3.5 years.
After Graduation
About 60% of our graduates continue in Master/PhD programs. Half of them prefer to continue their education in Tsukuba while others joined highly ranked universities in the USA and Western Europe. The other students decided to work, either in Japan or in their home countries.
Why Geoscience in Japan?
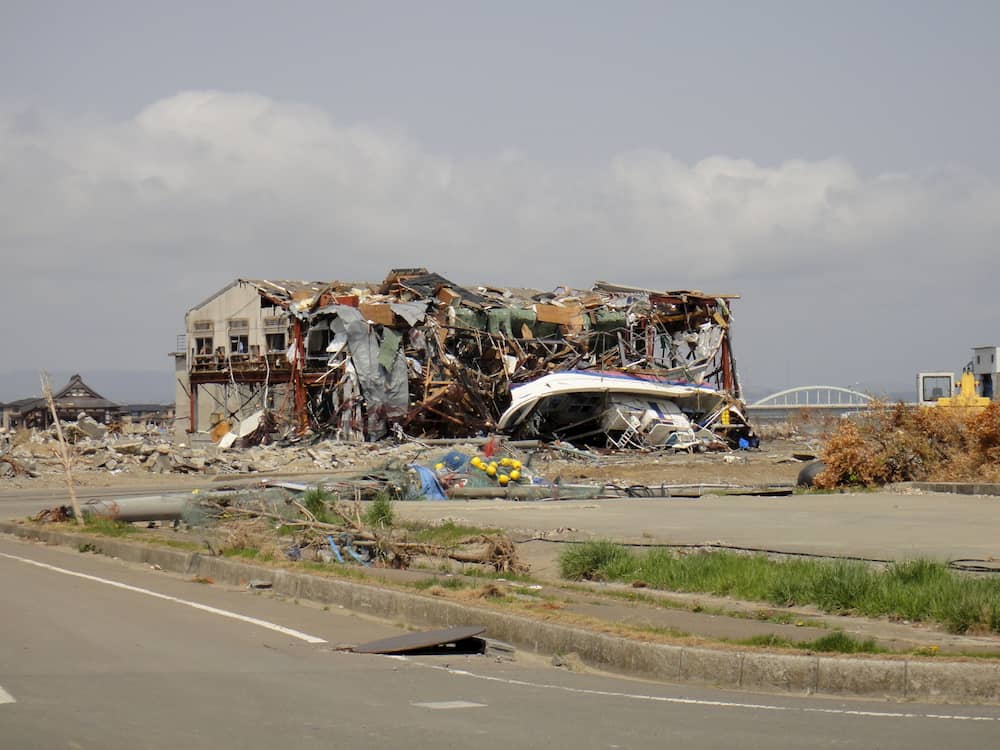

Disaster-Prone Country in Need of Geoscience
Japan is well known for its unique culture that combines tradition, nature and technology. This mountainous island country is located on an active margin with limited area suitable for agricultural, industrial or residential use and possesses limited natural resources. The forces of nature have attacked the human society of Japan throughout its history as natural disasters, for example, earthquakes, tsunamis, volcanic eruptions, typhoons/heavy rainstorms and associated floods, landslides, and other disaster types. Natural processes have also triggered human-related disasters such as the tsunami-induced nuclear plant accident in 2011 or coastal erosion. Such a natural and social background has required and promoted the development of various aspects of geoscience in Japan to solve pressing issues in densely populated areas.

Why Geoscience at University of Tsukuba?
Offering an Undergraduate Program in English

The University of Tsukuba is the only university in Japan offering an undergraduate degree in geoscience in English. The 4-year program in English started in 2011 and is now well established. The program is aimed at students who hold a non-Japanese passport. Knowledge of Japanese is not expected.
Outstanding Research at the International Level

The College of Geoscience of the University of Tsukuba is top-ranked in Japan and is known for its outstanding research at the international level. Pioneering research of our College includes earthquake physics, weather forecasting, forest hydrology, permafrost creep, GIS Science (Geographical Information System Science), environmental survey after the nuclear plant accident, and many more.
Covering the Whole Range of Geoscience

The College has 2 fields, 12 labs, and 43 academic staff, and covers a whole range of geoscience from paleontology, petrology, and atmosphere science to human/regional geographies.
Interested in Disasters?

We have experts who study natural/human-related disasters from a scientific point of view. We also offer a lecture on natural hazards in the English program.
Low Student-to-Staff Ratio

The staff number of 43 is high by international standards. According to governmental regulations the College of Geoscience is allowed to accept only 50 students per year in total for both the Japanese and English undergraduate programs. This equates to a low student-to-staff ratio of ~1.2 for the 1st-year intake. The low ratio helps students to cultivate closer relationships with their academic staff, have quicker access to feedback, and get involved in more interactive courses and discussions.
Large Variety of Field Work Courses
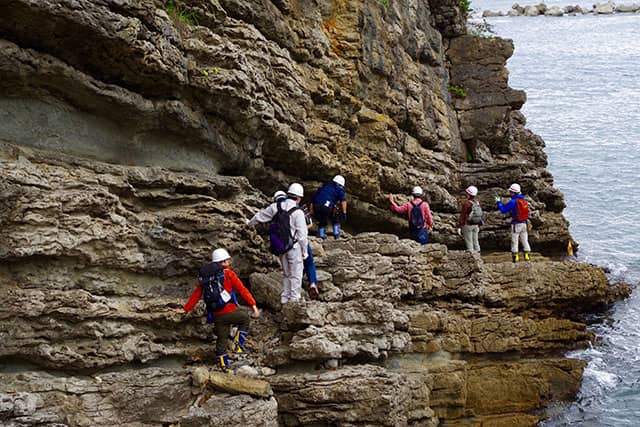

The foundation of geoscience is to analyze actual phenomena on the Earth. We offer many fieldwork courses in and outside of Japan every year to make observations and measurements, to explore Earth’s material and its structure, and to collect samples for further processing and analysis in laboratories.
Wide Variety of Skills and Knowledge
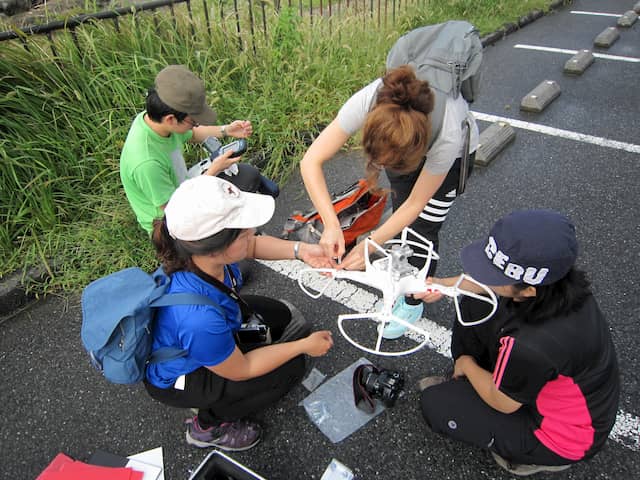

From basics to applications, there are many opportunities to acquire a wide variety of experiences, skills, and knowledge through various lectures, laboratory experiments, fieldwork, and seminars.
Take the First Step to Become a Geoscience Expert
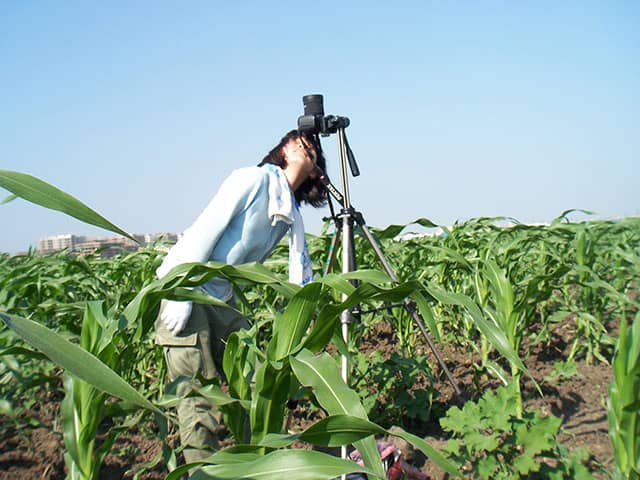

Graduation research, the first step for a geoscience expert, helps you to improve your scientific approaches and to develop writing and presentation skills. The research topics offered in the College of Geoscience are diverse, and so are the methods, from fieldwork to laboratory experiments, numerical simulations and literature surveys.
Research fields
2 Fields, 12 Laboratories, 43 Professors
The College of Geoscience comprises two fields of study: Geoenvironmental Sciences and Earth Evolution Sciences. Geoenvironmental Sciences explore the nature of, and processes in, the atmosphere, hydrosphere and the Earth’s surface as well as their interaction with human and biological activities. Earth Evolution Sciences study the structure, composition, history and mechanics of the Earth by quantitative geological, physical, chemical and biological methods for forecasting the future. Each field has 6 labs, and most labs have multiple professors. The total number of academic staff members is 43.
Geoenvironmental Sciences
Atmospheric Science
Research is conducted on various weather and climate phenomena that occur on regional to global scales. Research is done through the observation of weather in the subject area, various data analyses and numerical simulations using models.
Geomorphology
Geomorphology is the study of the forms of the land surface, the materials they consist of, and the processes which produce and modify them. Process geomorphology analyses the mechanics of geomorphic processes, whereas historical geomorphology focuses on histories or trajectories of landscape evolution. Applied geomorphology analyses, manipulates, and predicts geomorphic processes, which affect and are affected by human activities. In our laboratory we cover all three approaches by field work, laboratory experiments and analysis using Geographical Information Systems. Our main focus is on landforms related to weathering, landslides, gully erosion, sedimentary processes and ground freezing.
Hydrological Science
Our interests are the water cycle and terrestrial hydrological processes such as rainfall-runoff, evaporation, infiltration into the soil, groundwater flow, and so on. The transport of substances (pollutants, dissolved inorganic compounds, and carbon dioxide, etc.) and their impacts on the environment are also the targets of our studies. Field studies are the main tools, but computer models, laboratory experiments are as important to solve hydrological problems.
Human Geography
The purpose is to comprehensively and systematically research the spatial characteristics that are created by humans and the ground, including the relationship with the natural environment. Research is conducted multilaterally through statistical analysis and investigations of materials using demonstrative methods based on fieldwork in topics such as cities, rural areas, social and economic activities transportation, and the relationship between human beings and the environment.
Website: Japanese
Regional Geography
Regional Geography reveals the comprehensive man-land relationship from the viewpoint of a specific region while focusing on the socio-economic differences in urban and rural areas. Amid globalization and technological innovation progress, our regional geography group is engaged in a variety of land-use change issues and subsequent problems on different scales. We are working on empirical analysis for various regions across the world such as Japan, Asia, Oceania, Europe and Americas.
Website: Japanese
Analysis of Environmental Dynamics
The objectives of our laboratory are to develop a deep understanding of dynamics and changes in the global and regional environments through analysis of water and material cycle on the Earth’s surface using environmental isotopes or integrating remote sensing and GIS techniques.
Earth Evolution Sciences
Paleobiological Science
Our research group aims to understand the history of the Earth and life using fossil materials. Through fieldworks and laboratory analyses, we elucidate both global and regional events of organisms in deep time.
Our laboratory covers both micro- and macro-paleontology. Micropaleontology is the study of microscopic fossils, such as fossil plankton, pollen, and conodonts. Dr. Sachiko Agematsu especially focuses on conodonts, which are an enigmatic animal group that diversified in Paleozoic, along with other microfossils. By establishing conodont taxonomy and biostratigraphy, Dr. Agematsu is aiming to understand life history in the ocean, such as mass extinction events in Phanelozoic and paleozoogeography from Paleozoic to today.
Dr. Kohei Tanaka, on the other hand, studies macro-paleontology. His specialty is fossil vertebrates (i.e., animals with backbones), particularly dinosaurs. Dr. Tanaka’s main projects include the evolution of reproductive strategies in the lineage of reptiles, dinosaurs, and birds, using fossil eggs, nests, and babies.
Website: Japanese
Sedimentary Geology
Paleogeosphere Science Laboratory conducts fundamental research on the earth’s surface history through various methods of sedimentology, sedimentary petrology and paleontology. Our major research topics are (1) tectonic history at continental margins in and around the Tethys Sea, (2) Paleoenvironmental changes in Paleozoic and Mesozoic oceans, and (3) History of earthquakes and tsunamis in Asia.
Website: Japanese
Geodynamics
We, Geodynamics Laboratory, study Earth’s dynamics, including, but not limited to, earthquakes, tsunamis, crustal deformation, and accretionary processes. We do an analysis of geophysical data, fieldwork, laboratory experiments, and deep ocean drilling, aiming at a better understanding of Geodynamics on a vast spatiotemporal scale.
Website: Japanese
Petrology
This laboratory focuses on the petrological studies of igneous rocks and metamorphic rocks, as well as on the geochemical study of volcanic hydrothermal systems. Main topics are the investigation and elucidation of the origin and generation mechanism of magmas in volcanic arc systems, and of the metamorphic conditions and processes associated with the formation of major orogenic belts. The research methods basically involve field observations and laboratory experiments.
Website: Japanese
Mineralogy
A mineral is a naturally occurring solid with a highly ordered atomic arrangement and definite but not fixed chemical composition. Studying minerals involves various aspects of sciences and industrial applications. The study that reveals the physical properties of minerals is fundamental to a deeper understanding of the Earth’s past, present, and future. The application of inorganic chemistry to industry such as photonic crystals, functional materials, and semiconductors brings about an affluent society and a hopeful future in the world. We welcome students with backgrounds in geology, physics, chemistry, and materials science.
Planetary Resource Dynamics
Our research interests include the field and laboratory studies of topics on the formation of ore deposits, and the concentration and dispersion of metals in the terrestrial and extraterrestrial environment.
Course Catalogue
Our degree offers a broad education in fundamental and applied aspects of the bioresource sciences. On this page, you can find a list of courses available in English.
Finance
Planning your finances for university studies can be difficult. Your main expenses will be tuition, accommodation rent, food and living expenses, travel, and personal expenses.
Tuition fees
Partial and full tuition waivers are available for high performing students with financial difficulties.
Scholarships
The University’s Tsukuba Scholarship is open to all students, and provides 60,000 yen per month living allowance. For first grade students, the scholarship period is September to March. Thereafter, the scholarship period would be from April to March.
There are a variety of other scholarships available to international students, and the university can help students apply. Please note that many scholarships require students to hold a student visa, so students who have a Japanese passport may not be eligible for some scholarships.
A list of scholarships can be found on the university’s main webpage.
Admissions Center
For details of admission, please visit the following web page of University of Tsukuba.
